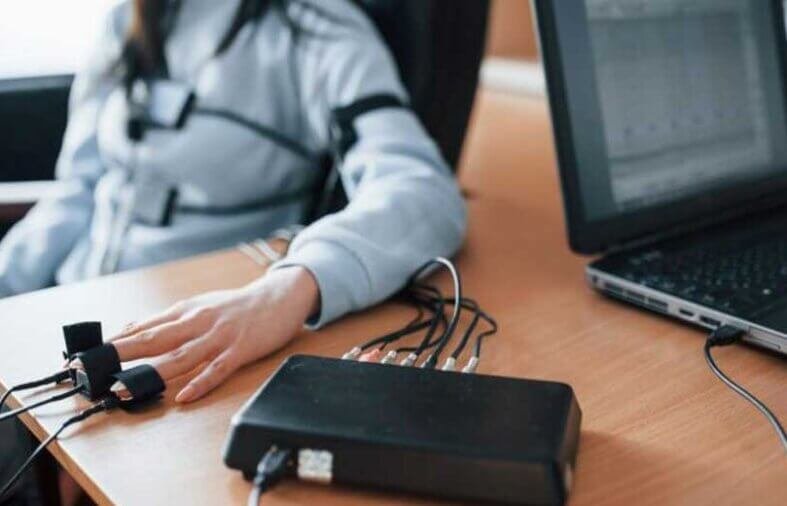
Lie detector tests, more formally known as polygraphs, have long been associated with determining whether someone is telling the truth or lying. They’re often depicted in movies and TV shows as an unassailable method of detecting deception. But what’s the reality behind these machines? How do they work, and more importantly, how accurate are they really?
How Do Lie Detector Tests Work?
Polygraph tests measure physiological responses that are believed to change when a person is stressed, anxious, or lying. The test typically involves the monitoring of several physical indicators:
- Heart rate: The number of beats per minute.
- Blood pressure: The force of blood against the walls of the arteries.
- Respiration rate: The pattern of breathing, including both the rate and depth of breath.
During the test, the individual is asked a series of questions while their physiological responses are recorded. The theory is that deceptive answers may cause changes in these physical responses — a spike in heart rate, for example — as the body reacts to the stress of trying to hide the truth. Make sure you contact professionals if you want to go ahead with a polygraph to ensure you get the best equipment available. For example, visit nationalprivateinvestigators.co.uk
However, these physical indicators can also be triggered by other factors like anxiety, fear, or even the act of being questioned. As a result, polygraph results aren’t necessarily indicative of deception but instead show changes in a person’s physiological state.
How Accurate Are Lie Detector Tests?
One of the biggest concerns with polygraph tests is their accuracy. While they’re often portrayed as infallible, the truth is much more nuanced.
Research has shown that polygraphs are not always reliable. In fact, some studies suggest that the accuracy rate of polygraph tests can vary widely, with estimates ranging from 70% to 90%. This means that in some cases, a polygraph might correctly identify a liar, but in other cases, it could give a false result — either falsely accusing an innocent person of lying (false positive) or failing to detect deception in someone who is actually lying (false negative).
The variability in results can stem from several factors:
- Individual differences: Some people’s physiological responses to stress may be less pronounced than others, meaning a polygraph could fail to detect their deception. On the flip side, someone who is nervous or anxious but not lying might produce physical responses that the polygraph interprets as signs of deceit.
- The examiner’s skill: Polygraph results are interpreted by examiners, who look for patterns in the physiological data. However, this interpretation is not always objective. An examiner’s experience, biases, and even their expectations can influence the results.
- Test conditions: External factors such as the environment (a quiet room versus a noisy one), the pressure to succeed, and even the subject’s understanding of how the test works can all impact results.
Is the Polygraph Useful?
Despite the challenges with accuracy, polygraphs are still used in certain contexts. In criminal investigations, polygraphs are often employed to help narrow down suspects or to verify alibis. In the workplace, especially for sensitive or security-related jobs, polygraph tests may be used to screen candidates.
However, polygraphs are not foolproof. Many experts agree that while they may provide helpful insights or help guide an investigation, they should never be relied upon as the sole piece of evidence in serious legal or professional decisions.
How to Get Someone to Take a Polygraph
Do you want someone in your life to take a polygraph? There can be several reasons why you think this is the answer. First, you think that they might be trying to deceive you and you’re not getting the truth from them. Alternatively, the relationship you have might already be damaged, which means you don’t believe anything they say. So, you want the lie detector test in order to ask questions and get the information you need to move on. Here are some tips on how you can get someone to take a polygraph.
Allow Them to Understand
One of the first things you can do with this person is tell them why you want them to take a polygraph. You need them to understand your reasons behind the decision so that they don’t refuse it straight away. Make sure that you’re not accusing the person, but it’s more about you gaining clarity in the situation.
Do Not Get Angry
One way that you’re going to convince someone not to take a lie detector test is if you’re angry. You don’t want to pressure them into taking it, and you don’t want to show that you’ll be angry afterwards. Reassure them that you just want answers and it’s about resolving the doubts you have. You need to promise that you won’t get mad and fly off the handle if there are things you don’t like.
Take the Test Too
Perhaps the person would feel more at ease if you also took the lie detector test. Indeed, taking it together can mean that you’re both being asked questions and find out whether you’re telling the truth. Perhaps there are some things that they want to know too and it can be a compromise between you.
Conclusion
Lie detector tests can be useful in certain situations, but their accuracy is far from guaranteed. The science behind polygraphs is based on the idea that physiological responses indicate deception, but in reality, there are many factors that can lead to inaccurate results. False positives, false negatives, and the inability to distinguish between stress caused by deception and stress caused by other factors make polygraphs an unreliable tool for determining truthfulness.
While they may still play a role in criminal investigations or job screenings, polygraph tests should be used with caution. The science behind them is not as definitive as many believe, and relying too heavily on polygraph results can lead to costly mistakes. For those seeking more reliable methods of detecting deception, exploring alternative technologies and techniques may be a better option.